What is a Paradigm Shift?
When using buzz words, they are most likely followed by words like “revolutionary” or “pradigm shift”. If one is living during such times, do they realize this? And how? A paradigm shift represents a profound change in the way people understand and approach problems within a particular field. Historically, paradigm shifts occur when existing models or systems fail to solve new, complex challenges, forcing a new approach that redefines the norms.
Examples from history include:
- The Printing Press: Made knowledge accessible to the masses, altering education and societal structures.
- The Industrial Revolution: Moved production from manual labor to machines, fundamentally changing industries and economies.
- The Internet: Transformed how people communicate, learn, and conduct business globally, bridging time and distance barriers.
In much the same way, AI agents represent a similar paradigm shift because they have the potential to transform how businesses operate, how employees work, and how customers interact with services, impacting all sectors and individuals.
How AI Agents Represent a Paradigm Shift
AI agents mark a significant evolution beyond earlier forms of automation, including rule-based systems like chatbots and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). While RPA was designed to automate repetitive, structured tasks, AI agents are designed to think, learn, and make decisions autonomously, performing complex tasks that require reasoning and adaptation.
AI agents differ from traditional automation because they can:
- Perceive and interact with their environment: They gather data from various inputs and use that data to reason about the best course of action.
- Learn from interactions: AI agents continuously learn from past experiences, adapting to changing conditions without the need for manual reprogramming.
- Execute complex decisions: Unlike RPA, which follows predefined rules, AI agents make independent decisions based on evolving inputs and goals.
This new paradigm expands the scope of automation, enabling AI agents to handle unstructured tasks — like responding to nuanced customer queries, analyzing market trends, or autonomously managing workflows across departments.
Business Process Automation: RPA vs. AI Agents
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has been a powerful tool for automating repetitive, well-defined tasks that follow a clear set of rules. For example, RPA bots can efficiently handle tasks like data entry, invoice processing, or routine customer support requests. However, RPA has limitations when it comes to unstructured data or situations that require complex decision-making.
AI agents move beyond the capabilities of RPA by introducing intelligence into automation. Here’s how they differ:
- RPA: Automates repetitive, structured tasks like processing transactions or extracting data from forms.
- AI agents: Handle complex, knowledge-based tasks that require reasoning, such as identifying patterns in data, generating insights, or autonomously executing multi-step workflows.
One of the key benefits of AI agents is their ability to adapt in real-time to changing conditions, something RPA cannot do. For instance, in a customer service environment, an RPA bot might answer basic questions, but an AI agent can understand nuanced queries, learn from previous interactions, and make personalized recommendations.
Can RPA and AI Agents Coexist?
Absolutely. In fact, many businesses are already using both RPA and AI agents to create seamless, end-to-end automation. While RPA excels at automating simple, repetitive tasks, AI agents are better suited to complex, dynamic processes that require decision-making and adaptability.
A typical example of their coexistence could be in finance:
- RPA might automate invoice data extraction and entry, while an AI agent reviews invoices, identifies discrepancies, and makes decisions on whether to approve or escalate payments based on business rules.
By combining RPA and AI agents, businesses can achieve more comprehensive automation across processes, enhancing both efficiency and decision-making capabilities.
AI Agents: The Future of Business Operations
AI agents are not just a tool for automation—they represent a fundamental shift in how businesses operate. Their ability to process vast amounts of data, reason through complex tasks, and learn from interactions means that they can autonomously manage workflows, support decision-making, and provide personalized customer experiences at scale.
Here’s how AI agents are revolutionizing business operations:
- Enhanced Efficiency: By taking on complex tasks like forecasting market trends, managing customer service, or even optimizing supply chains, AI agents reduce the workload on human employees while increasing operational efficiency.
- Greater Scalability: AI agents can easily scale across departments and functions, adapting to new tasks without needing extensive reprogramming.
- Personalization: In customer-facing roles, AI agents can provide more personalized service, learning from previous interactions and predicting customer needs more accurately than rule-based systems like RPA.
A Paradigm Shift in Technology
Beyond transforming business operations, AI agents also represent a profound shift in the technology landscape:
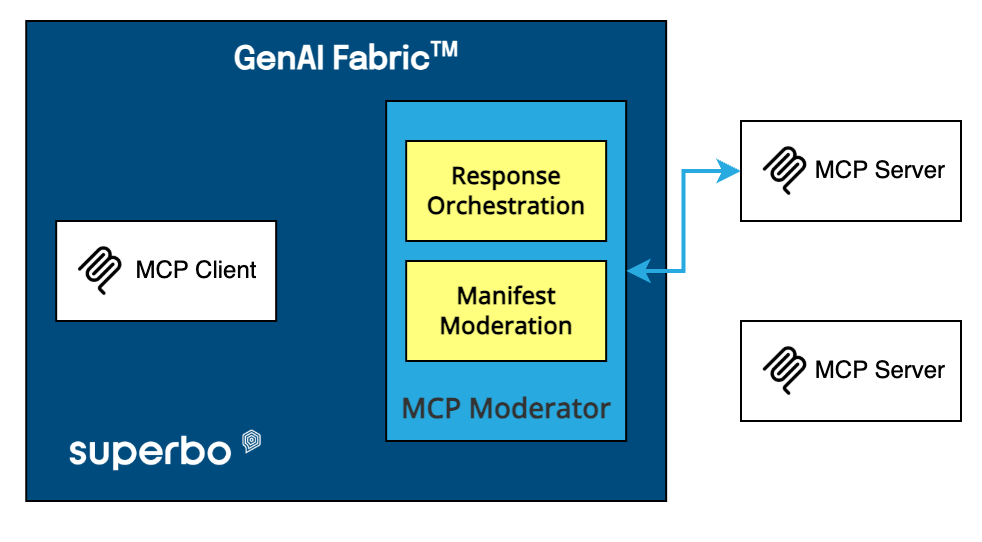
1. Evolution of System Architecture
AI agents require new technological infrastructures, including distributed computing environments, AI-specific chipsets, and generative AI models. These agents rely on advanced AI chips, such as Nvidia’s Tensor Cores, which enable the deep learning and neural network models that power their reasoning capabilities. System architectures supporting AI agents also need to manage multi-modal data processing, integrating text, voice, and visual inputs to make real-time decisions. This demands more from cloud infrastructures and storage systems than what is typically required for simpler applications.
2. Integration with Generative AI and LLMs
A key technological shift brought by AI agents is their dependence on Large Language Models (LLMs) and generative AI systems like GPT-4, which enable these agents to reason, communicate, and autonomously generate responses. This integration requires robust training models and continuous optimization to ensure that AI agents remain accurate and up-to-date, pushing AI model deployment strategies to new heights.
3. From Automation to Autonomy
AI agents represent the move from process automation to full autonomy in technology systems. Unlike RPA, which automates predefined tasks, AI agents adapt to unstructured environments, allowing for real-time learning and decision-making. This shift requires more complex software frameworks and self-correcting systems that are capable of independently navigating new challenges.
4. Real-Time Decision-Making and Adaptability
AI agents process vast amounts of data in real-time, enabling them to make decisions and adapt on the fly. This creates new technological demands for real-time data pipelines, cloud-based infrastructures, and AI-driven analytics, all of which must be capable of handling the computational and storage requirements of these intelligent systems.
Conclusion: A New Era of Automation and Technology
AI agents represent a paradigm shift not only for business operations but also for technology itself. By pushing the boundaries of what automation can achieve—through enhanced system architecture, generative AI, real-time learning, and autonomous decision-making—AI agents are reshaping the technology landscape.
As AI agents continue to evolve, they will drive both operational efficiency and technological innovation, becoming indispensable tools for companies aiming to remain competitive in an increasingly automated world. The future is agentic, and businesses that embrace this shift will be at the forefront of the next technological revolution.